In today’s data-driven landscape, migrating databases, whether to the cloud, a new platform, or an upgraded on-premise environment, is a critical yet daunting task. A single misstep can lead to costly downtime, data loss, and significant business disruption. This isn’t just a theoretical risk; industry reports suggest that over 60% of complex data migration projects run over budget or behind schedule. Furthermore, a Gartner analysis points to data loss in up to 40% of all migration projects, highlighting the urgent need for a structured, strategic approach.
This guide moves beyond generic advice to provide a comprehensive roadmap grounded in proven database migration best practices. We will break down the entire lifecycle into actionable phases, from initial assessment and planning to final cutover and post-migration optimization. For professionals working within the Microsoft ecosystem, including Power Platform Developers and Azure Specialists, the insights here are particularly relevant. We will leverage principles from Microsoft’s own frameworks, such as the Azure Database Migration Service documentation, to offer practical steps that transform a high-risk project into a strategic success.
By following these 7 essential practices, you will learn how to:
This listicle provides the detailed, actionable guidance necessary to execute a seamless and successful database migration, safeguarding your most valuable asset: your data.
A successful database migration is built on the foundation of meticulous planning and a comprehensive assessment of the existing environment. Skipping this foundational step is like building a house without a blueprint; the project is destined for scope creep, budget overruns, and potential failure. This phase involves a deep dive into the current database architecture, a clear understanding of business objectives, and a realistic evaluation of potential risks. It sets the stage for every subsequent action, from schema conversion to the final cutover.
This initial analysis is one of the most critical database migration best practices because it aligns technical execution with strategic business goals. According to a study by Microsoft, organizations that perform a detailed pre-migration assessment are 50% more likely to stay on budget and on schedule. The goal is to leave no stone unturned, creating a detailed roadmap that all stakeholders can understand and support.
Effective planning involves several core activities:
Capital One’s massive migration to the cloud is a prime example of planning at scale. Before moving a single byte of data, they spent over a year assessing more than 1,000 applications. This involved a comprehensive dependency mapping exercise to understand how each component interacted. This detailed upfront work enabled them to decommission eight data centers and move their operations to the cloud with minimal disruption, ultimately improving operational efficiency and innovation speed.
The following decision tree illustrates three non-negotiable checkpoints to validate before proceeding from the planning phase.
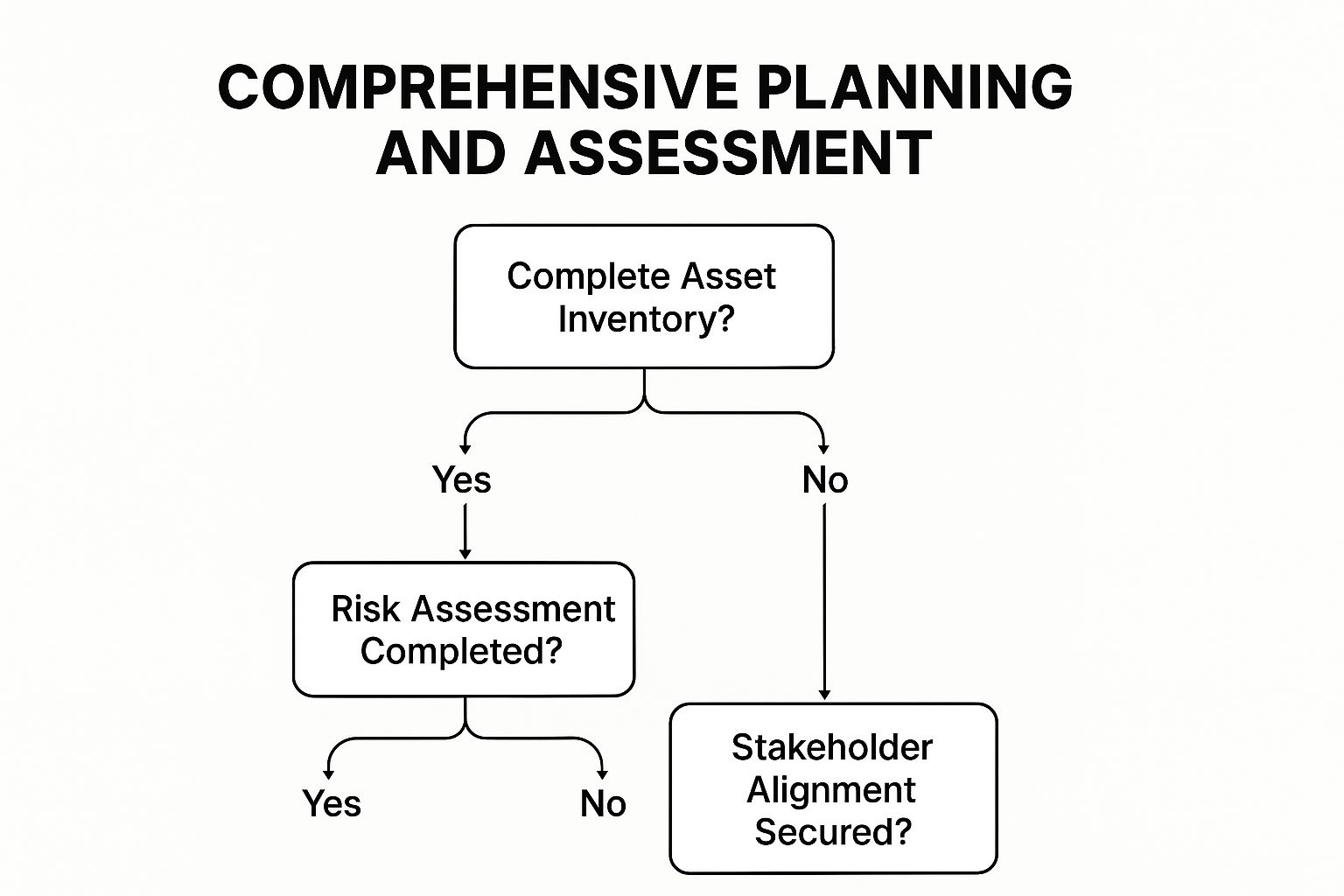
This visualization highlights that a migration project should only proceed if there is a complete asset inventory, a finalized risk assessment, and full stakeholder alignment, preventing costly rework later.
Selecting the most appropriate migration approach is a critical decision that directly impacts downtime, cost, risk, and user experience. There is no one-size-fits-all solution; the right strategy depends on a careful balance of business requirements, technical constraints, and data characteristics. Choosing correctly sets the project on a path to success, while a mismatch can lead to extended outages, data loss, and stakeholder dissatisfaction.
This strategic choice is a cornerstone of effective database migration best practices because it dictates the entire execution plan. Cloud service providers like Microsoft Azure heavily emphasize this decision point, as it determines the tools, timelines, and resources required. A well-chosen strategy minimizes disruption and aligns the technical process with the organization’s tolerance for downtime and risk.
Understanding the primary approaches is essential for making an informed choice:
When Microsoft IT migrated over 2,100 internal line-of-business applications to Azure, they didn’t rely on a single strategy. They employed a portfolio approach, using a big bang for smaller, non-critical apps and a phased strategy for complex, mission-critical systems. According to their published findings on the Microsoft IT Showcase, this hybrid model allowed them to optimize for speed while mitigating risk, achieving a 99.9% success rate on initial migrations and reducing operational costs by over 20%. This highlights the importance of tailoring the strategy to the specific application and business context.
A database migration is a high-stakes operation where data integrity is paramount. Implementing robust backup and recovery procedures is not just a safety net; it is a non-negotiable prerequisite for any migration project. This practice involves creating reliable, full backups of the source database before initiating the migration, establishing incremental backups during the process, and having a tested, documented plan to restore data or roll back the entire migration if a critical failure occurs.
This strategy is a cornerstone of responsible data stewardship and one of the most critical database migration best practices. It ensures that no matter what unexpected issues arise, from data corruption to application incompatibility, you can revert to a stable, known-good state with minimal business disruption. According to Microsoft’s guidelines for Azure database migrations, a verified backup and a practiced recovery plan can reduce recovery time by up to 75% in the event of a catastrophic failure during cutover.
A comprehensive strategy goes far beyond simply clicking “backup”:
During Slack’s migration of its core database infrastructure to Amazon RDS, the team placed immense emphasis on backup and recovery. They implemented automated backup validation scripts that would continuously restore backups to temporary instances and verify data consistency. This proactive approach ensured that every backup was not just created successfully but was also fully restorable. This rigorous process allowed them to proceed with the migration confidently, knowing they had a proven and reliable fallback mechanism at every stage, preventing potential data loss for millions of users.
A database migration isn’t complete until the data and applications are proven to work flawlessly in the new environment. Thorough testing and validation is the critical quality assurance phase that verifies data integrity, application functionality, and system performance post-migration. Treating testing as an afterthought introduces significant business risk, from corrupted data to application failures. This stage is about meticulously confirming that the new system not only works as expected but also meets or exceeds the performance and reliability of the old one.
This comprehensive verification process is one of the most vital database migration best practices because it prevents post-cutover disasters. According to a report by the Standish Group, inadequate testing is a leading cause of IT project failure. Microsoft’s own guidance highlights that successful migrations dedicate up to 40% of the project timeline to testing and validation to ensure a smooth transition. The objective is to identify and resolve issues before they impact end-users.
An effective validation strategy encompasses several distinct types of testing, each with a specific focus:
During its extensive migration to a new Kafka-based infrastructure, LinkedIn prioritized rigorous testing to avoid disrupting its massive user base. They employed extensive A/B testing, routing a small percentage of live traffic to the new system while keeping the old one as a fallback. This allowed them to compare performance and functionality in a real-world scenario with minimal risk. By gradually increasing traffic, they could validate stability and performance at scale, ensuring a seamless cutover for one of the world’s largest professional networks.
One of the most significant business risks in any database migration is the impact of downtime on operations and user experience. Strategic scheduling is the practice of meticulously planning and executing the migration cutover during periods of minimal business activity to reduce this impact. This approach moves beyond simply picking a weekend; it involves data-driven analysis of usage patterns, clear communication with stakeholders, and the use of technical strategies to ensure the transition is as seamless as possible.
This methodical scheduling is a cornerstone of effective database migration best practices because it directly addresses business continuity. According to a study by IDC, the average cost of critical application downtime can range from $500,000 to $1 million per hour for large enterprises. By carefully choosing the migration window and employing techniques like phased rollouts, organizations can significantly mitigate these financial and reputational risks, ensuring the project delivers value without disrupting the business it aims to improve.
Minimizing downtime requires a multi-faceted approach combining technical precision with business alignment:
GitHub’s migration of its primary MySQL database infrastructure is a masterclass in strategic scheduling and execution. To minimize impact on its millions of users, the engineering team planned the final cutover during a period of historically low traffic. They used a “dual-write” approach for weeks leading up to the migration, writing data to both the old and new databases simultaneously to ensure consistency. During the cutover window, they employed a custom tool called gh-ost to manage the final data synchronization and used a load balancer to gracefully shift traffic to the new primary database, completing the entire process with only a few seconds of user-facing downtime.
At the heart of any database migration is the data itself. Ensuring its integrity and consistency is not just a best practice; it is the fundamental objective. A migration that moves data but compromises its accuracy, completeness, or relational structure is a catastrophic failure. This phase involves implementing rigorous validation and reconciliation processes to guarantee that the data arriving in the target system is a perfect, trustworthy replica of the source data.
This focus on data quality is one of the most critical database migration best practices because it prevents data corruption, which can lead to flawed business reporting, application errors, and a loss of customer trust. According to a Gartner report, poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million annually. A migration is a high-risk event where these costs can be realized almost instantly if integrity checks are overlooked.
Effective data integrity assurance involves validation at multiple stages of the migration lifecycle:
When PayPal undertook a massive project to consolidate multiple database systems, data integrity was their highest priority. They implemented an extensive, multi-layered validation strategy. Before the cutover, they performed a full-scale “dry run” migration to a staging environment where they ran thousands of automated validation scripts. These scripts compared record counts, financial transaction summaries, and customer account balances between the source and target. This meticulous, automated reconciliation process ensured that when the live migration occurred, it was executed with zero data loss, preserving the trust of millions of users.
A database migration project can quickly become chaotic without a robust framework for documentation and communication. This practice involves meticulously recording every decision, procedure, and configuration, while simultaneously establishing clear and consistent communication channels with all stakeholders. Neglecting this aspect creates knowledge silos, complicates troubleshooting, and leaves the team unprepared for post-migration support or future projects.
This discipline is one of the most vital database migration best practices because it transforms a complex technical project into a transparent, collaborative effort. According to Microsoft, projects with a formal communication plan are significantly more likely to meet their original goals. Thorough documentation acts as the project’s institutional memory, ensuring that critical knowledge is retained long after the migration is complete, which is essential for ongoing maintenance and operational stability.
Effective execution requires a dual focus on creating accessible information and facilitating its flow:
When Twitch migrated its core infrastructure from a sharded PostgreSQL setup to a more scalable architecture, documentation was central to their success. The engineering team documented every step of their journey, including the challenges they faced with logical replication and the custom tooling they built.
This internal documentation became an invaluable resource for onboarding new engineers and troubleshooting production issues. It also served as the basis for public-facing engineering blogs, sharing knowledge with the wider tech community and reinforcing their position as a technical leader. By prioritizing documentation, Twitch not only ensured a smoother migration but also created a lasting asset for team training and knowledge transfer.
| Practice | Implementation Complexity | Resource Requirements | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive Planning and Assessment | High | High | Clear scope, timeline, risk mitigation | Large, complex migrations requiring alignment | Reduces surprises; realistic timelines; success criteria |
| Choose the Right Migration Strategy | Medium to High | Medium | Optimized timeline and resource usage; minimized disruption | Varies by business impact and downtime tolerance | Tailors approach; risk management; resource optimization |
| Implement Robust Backup and Recovery Procedures | Medium | High | Data protection; quick recovery | Critical data and compliance-sensitive migrations | Safety net; reduces risk; compliance support |
| Thorough Testing and Validation | High | High | Verified integrity, functionality, performance | Migrations requiring high reliability and confidence | Early issue detection; reduced bugs; confidence boost |
| Minimize Downtime with Strategic Scheduling | Medium | Medium | Reduced business impact and user disruption | Systems with high availability requirements | Less impact; better resource use; issue resolution time |
| Ensure Data Integrity and Consistency | High | Medium to High | Accurate, consistent, and reliable data | Projects where data quality is critical | Prevents data loss; supports audits; reduces data issues |
| Comprehensive Documentation and Communication | Medium | Medium | Knowledge transfer; stakeholder alignment | Projects with multiple teams and long timelines | Facilitates coordination; future reference; troubleshooting |
Successfully navigating a database migration is a testament to meticulous planning, disciplined execution, and a deep understanding of the underlying technology. This journey, moving from an abstract blueprint to a fully operational reality, is complex but manageable when approached with a structured methodology. By embracing the database migration best practices we’ve explored, you transform a high-risk technical challenge into a strategic business advantage, unlocking new capabilities, enhancing performance, and securing your data for the future.
The path we’ve detailed is a holistic one. It begins with Comprehensive Planning and Assessment, where you create the essential foundation for success. It progresses through choosing the Right Migration Strategy tailored to your specific business needs and technical constraints, and fortifying your project against disaster with Robust Backup and Recovery Procedures. Each of these initial steps is critical; a failure in planning will inevitably cascade through the entire project.
The theoretical planning phase gives way to practical execution with Thorough Testing and Validation, arguably the most crucial step for guaranteeing a smooth transition. This is where you proactively hunt down inconsistencies, performance bottlenecks, and functional errors before they can impact your users. According to Microsoft’s own guidance on migration projects, a well-structured testing phase can decrease post-cutover incidents by over 60%, a significant metric that directly impacts user trust and operational stability.
This focus on minimizing disruption is carried forward by Minimizing Downtime with Strategic Scheduling and ensuring Data Integrity and Consistency throughout the transfer process. These are not just technical goals; they are business imperatives. KPIs such as ‘Downtime Duration’ and ‘Post-Migration Error Rate’ are not merely numbers on a report. They represent real-world impacts on revenue, productivity, and customer satisfaction. A successful migration is one that is virtually invisible to the end-user.
Finally, the importance of Comprehensive Documentation and Communication cannot be overstated. This practice serves as the connective tissue for the entire project, ensuring all stakeholders are aligned, from developers and architects to business analysts and end-users. It creates a sustainable, manageable system long after the migration project is officially closed. Organizations that adopt a structured approach, like the one outlined in Microsoft’s Cloud Adoption Framework, consistently see tangible benefits, often reducing their migration timelines by 25-45% compared to ad-hoc efforts.
The ultimate goal of adopting these database migration best practices is not just to move data from point A to point B. It is to do so in a way that is secure, efficient, and aligned with broader business objectives. It’s about building a more resilient, scalable, and powerful data infrastructure that will serve as the foundation for future innovation. Your migration is not just a project; it’s a pivotal step in your organization’s digital transformation journey.
