Top 12 Low-Code Development Platforms for 2025
A Practical Guide for Microsoft Power Platform Professionals
The demand for rapid application development has far outpaced traditional coding, creating a need for faster, more efficient ways to build software. Low-code platforms fill this gap, allowing both professional and citizen developers to design and deploy applications quickly using visual interfaces and model-driven logic.
For Power Platform developers and architects, choosing the right tool is a strategic decision that affects scalability, governance, and integration across the Microsoft ecosystem.
A Microsoft-commissioned Forrester study found that organisations using Power Platform achieved a 188% return on investment over three years and a 74% reduction in development costs. Yet, in a crowded market of competing platforms, finding the best fit for your organisation remains a key challenge.
This guide highlights the 12 leading low-code platforms of 2025, comparing their strengths, limitations, pricing models, and best-fit scenarios—especially from a Microsoft perspective.
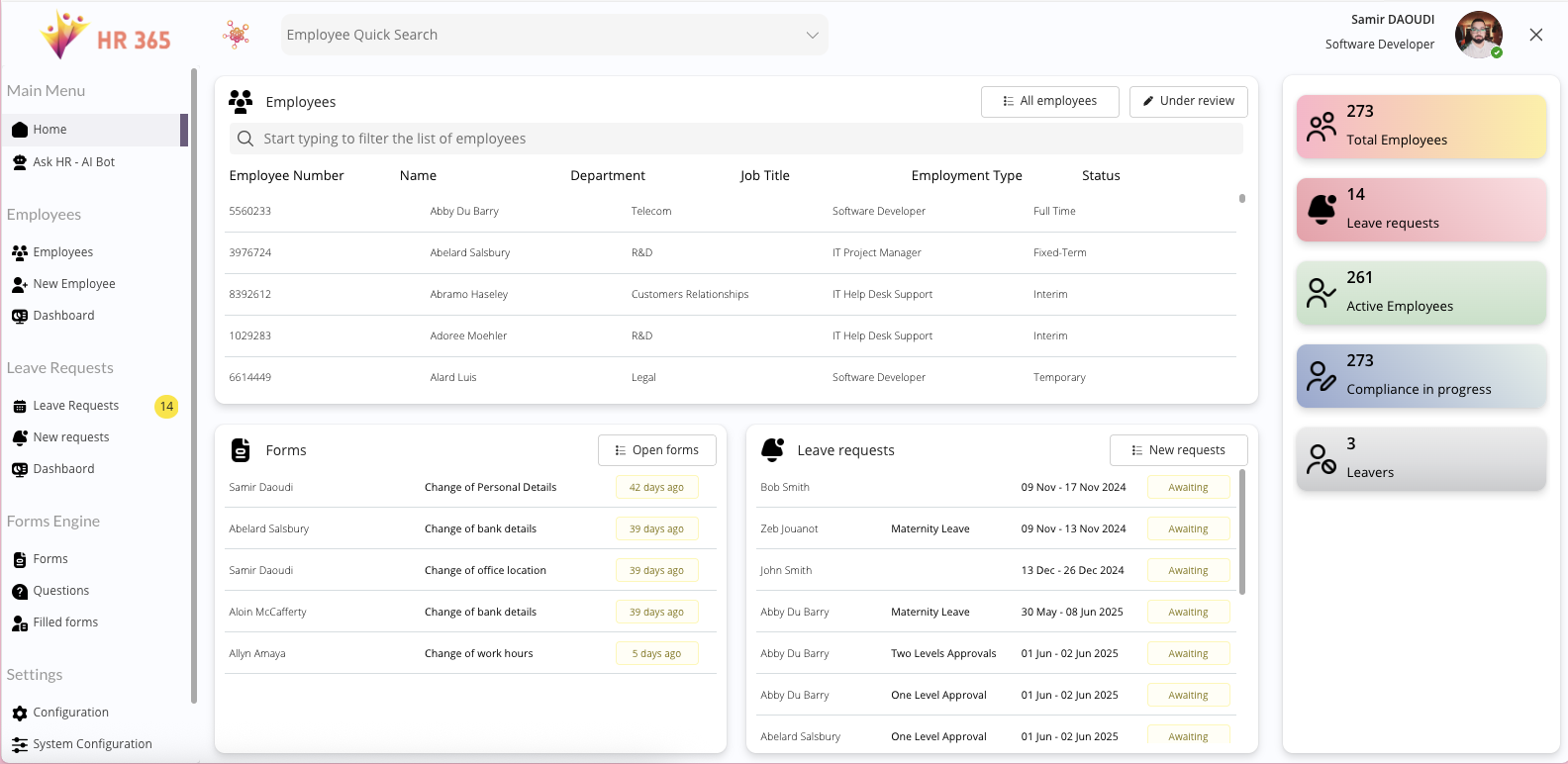
1. Microsoft Power Apps (Power Platform)
Power Apps is at the core of Microsoft’s low-code offering, enabling teams to build business applications rapidly with minimal code. It connects seamlessly with Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, Azure, and Teams, supporting single sign-on (SSO) and integration through more than 1,000 connectors.
Strengths: Enterprise-grade governance, DLP controls, and deep Microsoft integration.
Ideal Use Cases: Internal automation, mobile field apps, digitising manual workflows.
Pricing: Per-user, per-app, and pay-as-you-go models via Azure.
Limitations: Licensing complexity and limited design freedom for smaller teams.
🔗 microsoft.com/power-apps
2. Salesforce Platform (Lightning Platform)
Built within the Salesforce ecosystem, this platform allows developers to extend CRM functionality with Lightning App Builder and Flow.
Strengths: Deep CRM integration, large AppExchange marketplace, mature governance.
Ideal Use Cases: CRM extensions, partner or customer portals, automation workflows.
Pricing: Per-user with additional costs for add-ons.
Limitations: Steeper learning curve and higher costs for non-Salesforce users.
🔗 salesforce.com/platform
3. OutSystems
OutSystems offers a full-stack, enterprise-grade environment for building complex and high-performance applications. It includes built-in CI/CD, AI-assisted development, and multi-cloud support.
Strengths: Robust DevOps, performance monitoring, scalable architecture.
Ideal Use Cases: Core business systems, customer portals, legacy modernisation.
Pricing: Free for individuals; enterprise plans are customised.
Limitations: High entry cost and steeper learning curve.
🔗 outsystems.com
4. Mendix
Mendix enables collaborative, agile development across web and mobile, combining visual modelling with project management tools and flexible deployment options.
Strengths: Collaboration between business and IT, reusable components, and speed.
Ideal Use Cases: Enterprise systems, customer portals, and multi-experience apps.
Pricing: Free tier; paid plans scale by users and apps.
Limitations: Enterprise features require higher-tier licences.
🔗 mendix.com
5. Appian
Appian merges process automation, RPA, and app development in one environment, ideal for complex enterprise workflows.
Strengths: Unified automation, data fabric, and strong governance.
Ideal Use Cases: Case management, compliance systems, end-to-end automation.
Pricing: Free community edition; enterprise pricing on request.
Limitations: Limited design flexibility and bespoke quoting model.
🔗 appian.com
6. ServiceNow App Engine
ServiceNow App Engine extends the Now Platform, allowing teams to create secure workflow applications that automate processes across IT, HR, and finance.
Strengths: Strong governance, Integration Hub, and collaboration tools.
Ideal Use Cases: Workflow automation, employee service portals, IT operations.
Pricing: Enterprise-focused and quote-based.
Limitations: Best suited to existing ServiceNow customers due to complexity.
🔗 servicenow.com/app-engine
7. Zoho Creator
Zoho Creator provides an intuitive drag-and-drop builder for SMEs, allowing quick app creation with integrated mobile deployment and automation.
Strengths: Ease of use, affordability, and rapid deployment.
Ideal Use Cases: Internal dashboards, inventory tracking, and workflow apps.
Pricing: Free tier and competitively priced paid plans.
Limitations: Less suited to large-scale enterprise integrations.
🔗 zoho.com/creator
8. Airtable
Airtable blends spreadsheet simplicity with database power, helping teams manage data and build functional apps without coding.
Strengths: User-friendly interface, strong collaboration, and automation.
Ideal Use Cases: Project tracking, content management, and lightweight CRMs.
Pricing: Free and tiered paid plans.
Limitations: Record limits can restrict enterprise use.
🔗 airtable.com
9. Retool
Retool accelerates the creation of internal tools by combining drag-and-drop design with developer-level JavaScript flexibility.
Strengths: Excellent for data-driven dashboards and internal systems.
Ideal Use Cases: Admin panels, CRUD apps, and database GUIs.
Pricing: Builder/end-user model; enterprise plans for self-hosting.
Limitations: Primarily for internal apps; limited public-facing options.
🔗 retool.com
10. Google AppSheet
AppSheet enables users to build apps directly from spreadsheets or databases—ideal for mobile, data-driven processes.
Strengths: Fast prototyping, offline sync, and Google Workspace integration.
Ideal Use Cases: Field service, inspections, inventory, and approvals.
Pricing: Free for prototypes; tiered enterprise plans available.
Limitations: Less suited to complex relational logic or custom UI.
🔗 appsheet.com
11. Oracle APEX
Bundled with the Oracle Database, APEX allows developers to create high-performance, data-centric web applications directly within the database.
Strengths: Secure, scalable, and cost-effective—no per-user licence required.
Ideal Use Cases: Data-driven systems, reporting dashboards, Oracle app modernisation.
Pricing: Included with Oracle subscriptions; free tier on Oracle Cloud.
Limitations: Best for teams with SQL expertise.
🔗 apex.oracle.com
12. Quickbase
Quickbase unifies data, workflows, and teams to deliver operational agility across complex projects and compliance-heavy industries.
Strengths: Strong governance, workflow automation, and compliance support.
Ideal Use Cases: Project management, supply chain, and process optimisation.
Pricing: Tiered business and enterprise plans with free trial.
Limitations: Higher total cost for smaller teams.
🔗 quickbase.com
Platform Comparison
| Platform | Key Strength | Ideal For | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Apps | Deep Microsoft integration | MS enterprises | Flexible (Azure-based) |
| Salesforce Platform | CRM extensions | Salesforce users | Per-user + add-ons |
| OutSystems | Full-stack scalability | Large enterprises | Custom |
| Mendix | Agile collaboration | Enterprise teams | Usage-based |
| Appian | End-to-end automation | Regulated industries | Quote-based |
| ServiceNow App Engine | Workflow governance | ServiceNow clients | Enterprise quote |
| Zoho Creator | Ease and affordability | SMEs | Low-cost tiers |
| Airtable | Simplicity & collaboration | Teams & PMOs | Tiered |
| Retool | Developer control | Technical teams | Flexible |
| AppSheet | Data-driven mobility | Field teams | Tiered |
| Oracle APEX | SQL & database power | Oracle users | Included |
| Quickbase | Workflow automation | Large ops teams | Tiered |
Making the Right Choice
Selecting a low-code platform is more than a technical decision—it’s a long-term investment in your organisation’s agility and innovation capacity.
Key Evaluation Factors:
Technology Stack: Choose tools that complement your existing infrastructure.
Use Cases: Match capability to complexity—internal apps vs enterprise systems.
Team Skillset: Consider developer and business user proficiency.
Governance & ALM: Prioritise platforms with strong lifecycle and compliance tools.
Total Cost of Ownership: Account for licences, connectors, training, and scale.
The right low-code platform will not only speed up delivery but also enhance governance, empower teams, and drive sustained digital transformation.