7 Essential Microsoft 365 Security Best Practices for 2025
Discover our comprehensive list of Microsoft 365 security best practices. Learn to protect your data with MFA, Zero Trust, ATP, and more in this in-depth guide.
In the modern hybrid work environment, Microsoft 365 serves as the operational core for countless organizations. This centrality, however, also makes it a prime target for increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. A reactive, “set-it-and-forget-it” security posture is no longer sufficient to protect sensitive data and user identities. This guide provides a detailed roundup of the most critical microsoft 365 security best practices you must implement to build a resilient and proactive defense.
We will move beyond generic advice, offering actionable steps, real-world statistics, and official Microsoft references to fortify your digital fortress. For instance, Microsoft’s own data reveals a crucial insight: enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) can block over 99.9% of account compromise attacks. This single statistic underscores the immense power of a layered, modern security strategy, which is the central theme of our discussion.
Throughout this comprehensive listicle, we will explore seven equally vital practices that form the pillars of a secure M365 ecosystem. You will learn how to:
- Implement a Zero Trust architecture to verify every access request explicitly.
- Configure Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) to shield against phishing and malware.
- Establish robust Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies to prevent data exfiltration.
- Manage high-risk permissions with Privileged Access Management (PAM).
By the end of this article, you will have a clear, actionable roadmap for implementing these essential microsoft 365 security best practices, ensuring your data, users, and organization are protected against both current and emerging threats. We’ll provide the specific details needed to move from theory to practical application, safeguarding your collaborative environment.
1. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing robust Microsoft 365 security best practices starts with a foundational layer of protection: Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). MFA strengthens access security by requiring two or more verification methods to prove a user’s identity. This layered defense means that even if a cybercriminal steals a user’s password, they likely won’t be able to access the account without the second factor.
According to Microsoft, enabling MFA can block over 99.9% of account compromise attacks. It moves security beyond a single point of failure (the password) and introduces a significant barrier for unauthorized access attempts. This is crucial in today’s environment where phishing and credential theft are rampant.

Why MFA is a Non-Negotiable First Step
A compromised account is a gateway to your entire digital estate, from sensitive emails in Exchange Online to confidential files in SharePoint and OneDrive. For organizations handling regulated data, like healthcare providers needing HIPAA compliance or financial institutions, MFA is often a mandatory requirement. A key KPI for security teams should be the “MFA adoption rate,” aiming for 100% coverage for all users, especially administrators.
This infographic illustrates the common methods used to satisfy the “something you have” requirement in MFA.

The visualization highlights the diversity of MFA methods, from widely accessible SMS codes to highly secure hardware tokens, allowing organizations to choose the right balance of security and user convenience.
Practical Implementation Tips
A successful MFA deployment requires careful planning and communication. Rushing a rollout can lead to user friction and helpdesk overload.
- Pilot Program: Begin with a small, tech-savvy pilot group (like the IT department) to identify potential challenges and refine your communication strategy before a company-wide deployment.
- Clear User Guidance: Develop straightforward instructions, FAQs, and short training videos. Explain why MFA is being implemented, focusing on the protection it offers both the company and the individual user.
- Conditional Access Policies: Use Azure AD Conditional Access to ease into MFA. You can start by requiring it only for risky sign-ins, access from untrusted locations, or for users accessing highly sensitive applications. This targeted approach minimizes initial disruption.
- Explore Passwordless Options: For a more seamless user experience, consider modern passwordless methods like Windows Hello for Business, FIDO2 security keys, or the Microsoft Authenticator app. For a deeper dive into modern authentication, explore these advanced password protocols in Microsoft products.
2. Implement Zero Trust Architecture
Transitioning from a traditional perimeter-based security model to a modern approach requires adopting a Zero Trust architecture. This security framework operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” assuming that a breach is inevitable or has already occurred. It treats every access request as originating from an untrusted network, requiring continuous verification for every user, device, application, and data transaction.
In the context of Microsoft 365, Zero Trust means moving beyond the idea of a secure corporate network. Instead, security policies are applied based on the identity of the user, the health of their device, the application they are accessing, and other real-time signals, regardless of their location. Microsoft’s own internal implementation of Zero Trust resulted in a 50% reduction in security incidents while enabling a massive shift to remote work, proving its effectiveness at scale.
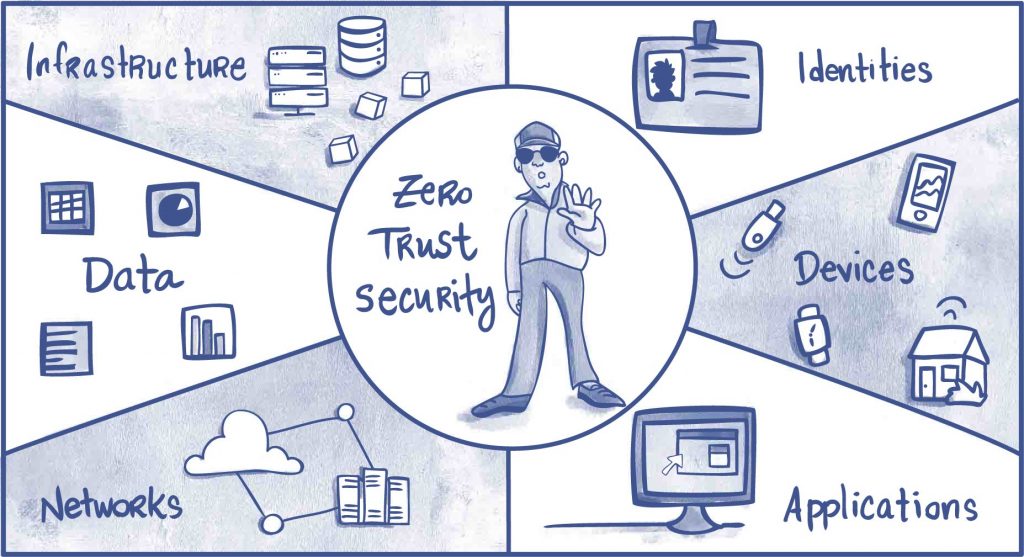
Why Zero Trust is a Modern Security Imperative
In a cloud-first world, the network perimeter has dissolved. Employees, partners, and contractors access resources from various locations using a mix of corporate and personal devices. A Zero Trust model directly addresses this reality by securing the data and resources themselves. For instance, a global consulting firm successfully used Zero Trust principles to grant contractors secure, VPN-less access to specific SharePoint sites, limiting their access to only what was necessary and continuously verifying their identity and device compliance.
This approach is not just a best practice; it is increasingly a standard. Government agencies are now mandated to adopt Zero Trust architectures to meet federal cybersecurity requirements, highlighting its importance in protecting critical infrastructure and sensitive information.
Practical Implementation Tips
Implementing Zero Trust is a journey, not a destination. It involves a gradual, phased approach rather than a single deployment.
- Start with Identity: Treat identity as your primary security perimeter. Enforce strong authentication like MFA (as discussed in the previous point) and use Azure AD Conditional Access as the central policy engine for your Zero Trust strategy.
- Implement Device Compliance: Use Microsoft Intune to define and enforce device health and compliance policies. You can then use Conditional Access to block access from non-compliant or unhealthy devices, ensuring only trusted endpoints can connect to your data.
- Apply Least Privilege Access: Configure roles and permissions in SharePoint, Teams, and other M365 services to ensure users have only the minimum level of access required to perform their jobs. Regularly review these permissions to prevent privilege creep.
- Monitor and Analyze Logs: Continuously monitor Azure AD sign-in logs, audit logs, and Microsoft Defender signals to understand access patterns, detect anomalies, and respond to threats in real time. For more information on this approach, review Microsoft’s Zero Trust deployment guidance.
3. Configure Advanced Threat Protection (ATP)
Beyond standard email filtering, a critical component of modern Microsoft 365 security best practices involves deploying a proactive defense against sophisticated, zero-day threats. Microsoft Defender for Office 365, formerly known as Advanced Threat Protection (ATP), provides this crucial layer. It uses powerful machine learning, real-time threat intelligence, and sandboxing technology to analyze and neutralize advanced attacks like targeted phishing, business email compromise, and polymorphic malware before they can impact your organization.
This advanced security suite goes far beyond traditional signature-based antivirus. It preemptively detonates suspicious attachments in a virtual environment (Safe Attachments) and rewrites URLs to check them against a constantly updated list of malicious sites at the time of click (Safe Links). According to Microsoft, Defender for Office 365 blocks an average of 32 billion email threats per year, demonstrating its massive scale and effectiveness.

Why ATP is Essential for Proactive Defense
Relying solely on default email protection is insufficient against today’s targeted cyberattacks. Defender for Office 365 is designed to stop the threats that standard filters miss, safeguarding your most vulnerable entry point: your users’ inboxes. A key performance indicator (KPI) here is the “mean time to detect” (MTTD) threats; ATP aims to reduce this to near-zero for known and emerging email-based attacks.
The effectiveness is backed by Microsoft’s own data, which shows that organizations using Defender for Office 365 have a significantly lower compromise rate. It acts as a critical backstop, protecting sensitive data within Exchange, SharePoint, and Teams from being compromised via a malicious link or attachment.
Practical Implementation Tips
A properly configured Defender for Office 365 deployment can dramatically improve your security posture without creating unnecessary friction for users.
- Configure Safe Attachments: Start by setting up a Safe Attachments policy and choose the “Dynamic Delivery” option. This sends the body of the email to the recipient immediately while the attachment is scanned, minimizing delays and maintaining user productivity.
- Implement Safe Links Broadly: Apply Safe Links policies not just to email but also to Office 365 applications like Word, Excel, and Teams. This ensures users are protected regardless of where they encounter a malicious link within the M365 ecosystem.
- Create Targeted Anti-Phishing Policies: Establish a custom anti-phishing policy with stricter settings, including impersonation protection, for high-value targets like executives, finance department staff, and administrators.
- Leverage Threat Intelligence: Regularly use Threat Explorer to analyze attack campaigns targeting your organization. For deeper insights, you can learn more about how to stay ahead of cyberattacks with Office 365 threat intelligence.
- Run Attack Simulations: Use the built-in Attack Simulation Training to send realistic but benign phishing campaigns to your users. This helps identify vulnerable users and provides targeted training to improve security awareness across the board.
4. Establish Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies
Securing user identities is critical, but protecting the data itself is an equally important pillar of Microsoft 365 security best practices. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies provide a sophisticated safety net, helping organizations identify, monitor, and automatically protect sensitive information across services like Exchange Online, SharePoint, OneDrive, and Microsoft Teams. DLP prevents the accidental or malicious sharing of confidential data, acting as a digital guardian for your most valuable assets.
Microsoft Purview Data Loss Prevention can identify sensitive items by using deep content analysis, not just by a simple text scan. It uses keyword matches, dictionary matches, regular expressions, and internal functions to detect content that matches your DLP policies. This automated intelligence is crucial for preventing data leaks before they happen.
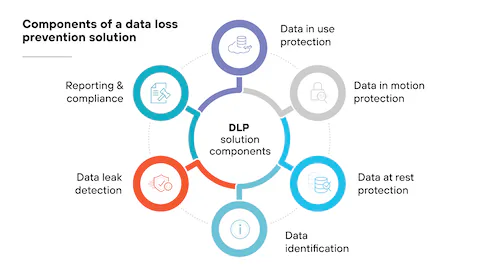
Why DLP is Essential for Data Governance
In a world of constant collaboration, the risk of sensitive data exposure is higher than ever. An employee might accidentally email a spreadsheet with customer social security numbers to an external contact or save a document containing proprietary intellectual property to a personal cloud storage account. DLP policies help mitigate these risks automatically, enforcing organizational data handling rules without constant manual oversight.
For instance, a healthcare organization can use DLP to prevent HIPAA violations by creating a policy that blocks any email containing patient health information from being sent outside the company network. A valuable KPI to track is the “number of DLP policy matches” and “override incidents,” which helps gauge user behavior and policy effectiveness.
Practical Implementation Tips
A well-planned DLP strategy minimizes business disruption while maximizing data protection. A “boil the ocean” approach can create friction, so a phased rollout is recommended.
- Start in Test Mode: Begin by running your DLP policies in “test mode” without policy tips. This allows you to monitor and assess the impact of the policy using DLP reports, helping you understand data flow patterns before you start blocking actions or notifying users.
- Leverage Built-in Templates: Microsoft provides a rich library of pre-configured DLP templates for common regulations and data types (like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS). Start with these templates before creating complex custom policies from scratch.
- Educate and Empower Users: Combine policy enforcement with user education. Configure policy tips to appear in real-time, informing users when they are about to share sensitive information and guiding them toward compliant actions. This proactive approach builds a security-conscious culture.
- Refine and Iterate: Data security is not a “set it and forget it” task. Regularly review DLP reports and incident logs to identify false positives, discover new data handling patterns, and fine-tune your policies for better accuracy and effectiveness. For more detailed guidance, refer to Microsoft’s official documentation on designing a data loss prevention policy.
5. Implement Privileged Access Management
Another critical component of a comprehensive Microsoft 365 security best practices strategy is implementing Privileged Access Management (PAM). PAM provides granular control over administrative access by granting privileges only when needed, for a limited time. This “just-in-time” (JIT) approach drastically reduces the attack surface associated with standing administrative privileges.
Standing access means that accounts with high-level permissions, like Global Administrator, are always active. If one of these accounts is compromised, the attacker gains persistent, unrestricted access to your entire tenant. PAM mitigates this risk by ensuring privileged roles are inactive until an administrator explicitly requests, justifies, and is approved for temporary elevation.
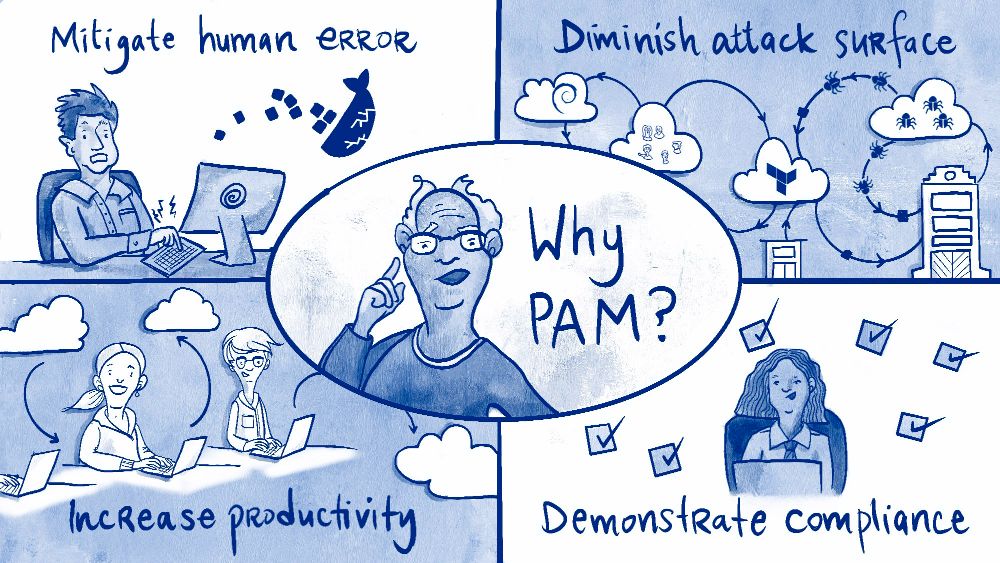
Why PAM is Essential for High-Stakes Environments
Privileged accounts are the prime targets for sophisticated attackers. A single compromised admin account can lead to catastrophic data breaches, service disruptions, and reputational damage. By enforcing an approval workflow and time-bound access, PAM minimizes the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit these powerful credentials. It also creates a clear audit trail for every privileged action taken.
According to Microsoft, organizations should aim to have fewer than five global administrator accounts to reduce their attack surface. A key KPI for PAM is the “percentage of standing privileged roles converted to JIT-eligible,” with a goal of minimizing standing access as much as possible.
Practical Implementation Tips
Deploying PAM effectively requires a shift in administrative habits and clear policies. Careful planning ensures a smooth transition to this more secure operational model.
- Identify and Inventory Privileged Roles: Begin by identifying all accounts with high-impact roles (e.g., Global Admin, SharePoint Admin, Exchange Admin). Your goal is to minimize the number of accounts with standing privileges.
- Configure JIT Access in Azure AD: Use Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM) to configure roles for JIT activation. Define approval workflows, set maximum activation durations, and require justification for every request.
- Establish Emergency Access Procedures: Create “break-glass” accounts for emergency scenarios. These accounts should be highly secured, monitored, and used only when normal administrative access procedures fail.
- Configure Alerts and Reviews: Set up automated alerts to notify security teams whenever a privileged role is activated. Schedule regular access reviews using Azure AD to ensure that role assignments remain appropriate and necessary over time. For more information on structuring permissions, you can explore the fundamentals of properly implementing Role-Based Access Control.
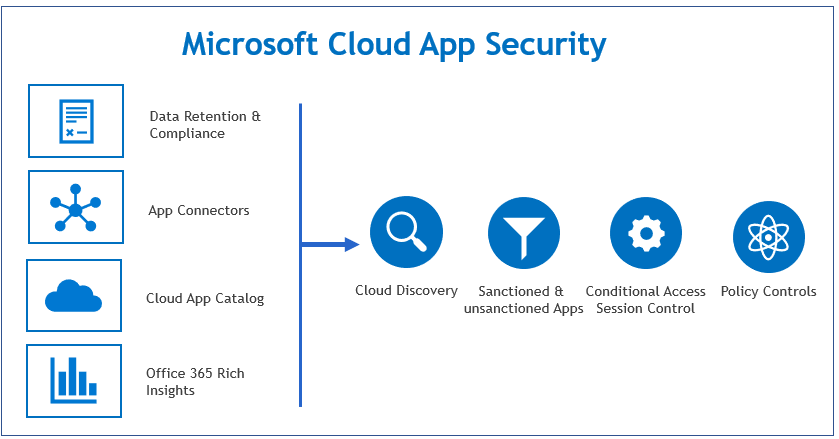
6. Enable Cloud App Security (CASB)
One of the most critical Microsoft 365 security best practices is to harness the power of a Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB). Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps is Microsoft’s native CASB solution, providing essential visibility, data control, and threat protection for your cloud applications. It acts as a gatekeeper between your users and cloud services, allowing you to monitor activity and enforce granular security policies.
In an era of “shadow IT,” where employees often use unsanctioned cloud apps, Defender for Cloud Apps discovers this usage and assesses the risk of over 31,000 cloud applications. This visibility is the first step toward regaining control over your corporate data as it moves through the cloud ecosystem.
Why DLP is Essential for Data Governance
In a world of constant collaboration, the risk of sensitive data exposure is higher than ever. An employee might accidentally email a spreadsheet with customer social security numbers to an external contact or save a document containing proprietary intellectual property to a personal cloud storage account. DLP policies help mitigate these risks automatically, enforcing organizational data handling rules without constant manual oversight.
For instance, a healthcare organization can use DLP to prevent HIPAA violations by creating a policy that blocks any email containing patient health information from being sent outside the company network. A valuable KPI to track is the “number of DLP policy matches” and “override incidents,” which helps gauge user behavior and policy effectiveness.
Practical Implementation Tips
A well-planned DLP strategy minimizes business disruption while maximizing data protection. A “boil the ocean” approach can create friction, so a phased rollout is recommended.
- Start in Test Mode: Begin by running your DLP policies in “test mode” without policy tips. This allows you to monitor and assess the impact of the policy using DLP reports, helping you understand data flow patterns before you start blocking actions or notifying users.
- Leverage Built-in Templates: Microsoft provides a rich library of pre-configured DLP templates for common regulations and data types (like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS). Start with these templates before creating complex custom policies from scratch.
- Educate and Empower Users: Combine policy enforcement with user education. Configure policy tips to appear in real-time, informing users when they are about to share sensitive information and guiding them toward compliant actions. This proactive approach builds a security-conscious culture.
- Refine and Iterate: Data security is not a “set it and forget it” task. Regularly review DLP reports and incident logs to identify false positives, discover new data handling patterns, and fine-tune your policies for better accuracy and effectiveness. For more detailed guidance, refer to Microsoft’s official documentation on designing a data loss prevention policy.
7. Establish Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
To achieve a comprehensive and proactive security posture, organizations must move beyond individual alerts to a centralized, intelligent view of their entire digital environment. This is where a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution, like Microsoft Sentinel, becomes a critical component of your Microsoft 365 security best practices. It provides a single pane of glass for threat detection, visibility, and response by collecting and analyzing security data at cloud scale.
Microsoft Sentinel is a cloud-native SIEM that ingests data from across your entire organization, including Microsoft 365 services, Azure, endpoints, and other third-party sources. It uses built-in artificial intelligence to correlate alerts, detect multi-stage attacks, and hunt for threats that might otherwise go unnoticed. This bird’s-eye view transforms security from a reactive, alert-by-alert firefight into a proactive, intelligence-driven operation.
Why Centralized SIEM is a Modern Security Imperative
In a complex environment like Microsoft 365, security signals are generated constantly from Exchange Online, SharePoint, Teams, and Azure Active Directory. Without a SIEM, these signals exist in silos, making it nearly impossible to connect the dots of a sophisticated attack. A SIEM aggregates this data, allowing security teams to identify patterns and respond swiftly. According to Microsoft, customers using Sentinel see up to a 90% reduction in alert fatigue and an 80% lower cost compared to legacy SIEMs.
This centralized intelligence is not just for threat hunting; it’s also essential for compliance. Government agencies have used Sentinel to gain unified visibility across multiple M365 tenants, simplifying the process of demonstrating adherence to stringent regulatory requirements.
Practical Implementation Tips
Deploying a SIEM can seem daunting, but a phased approach focused on high-value data sources can yield immediate benefits. A successful implementation relies on strategic configuration and continuous refinement.
- Start with Microsoft 365 Data Connectors: Begin by enabling the built-in data connectors for key services like Azure AD Identity Protection, Microsoft Defender for Office 365, and Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps. These connectors are easy to configure and provide immediate, high-fidelity security data.
- Leverage Built-in Analytics Rules: Before building complex custom detections, activate and tune the analytics rules templates provided by Microsoft. These rules are based on common attack vectors and Microsoft’s extensive threat intelligence, offering a strong baseline for threat detection.
- Implement SOAR Playbooks: Use Sentinel’s Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) capabilities to automate common tasks. Create playbooks to automatically enrich alerts with user risk data, block a compromised IP address, or isolate an affected endpoint, freeing up your analysts for more complex investigations.
- Train Your Team on KQL: To unlock the full potential of threat hunting in Sentinel, your security team must become proficient with the Kusto Query Language (KQL). Invest in training to enable them to proactively search for indicators of compromise and build custom detection logic tailored to your environment. You can find extensive learning resources on Microsoft Learn.
- Configure Data Retention Policies: Actively manage your data retention settings in the Log Analytics workspace to balance security requirements with cost. Determine how long you need to retain data for compliance and forensic purposes to avoid unnecessary storage expenses.